This is the second part of the probability series, in the first segment we discussed the basic concepts of probability. In this second part we will delve deeper into the topic and discuss the theorems of probability. Let’s find out what these theorems are.
Addition Theorem
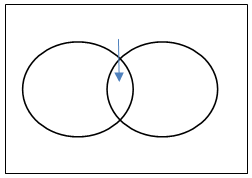
Removing the intersections will give the probability of A or B or both.
Example:- From a deck of cards 1 card is drawn, what is the probability the card is king or heart or both?
Total cards 52
P(KingUHeart)= P(King)+P(Heart) ─ P(King∩Heart)
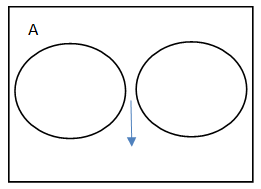
- If A and B are two mutually exclusive events then the probability that either A or B will occur is the sum of individual probabilities of the events A and B.
P(A)+P(B), here the combined probability of the two will either give P(A) or P(B)
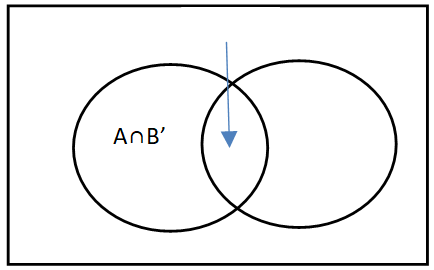
- If A and B are two non mutually exclusive events then the probability of occurrence of event A is given by
Where B’ is 1-P(B), that means probability of A is calculated as P(A)=1-P(B)
Multiplication Law
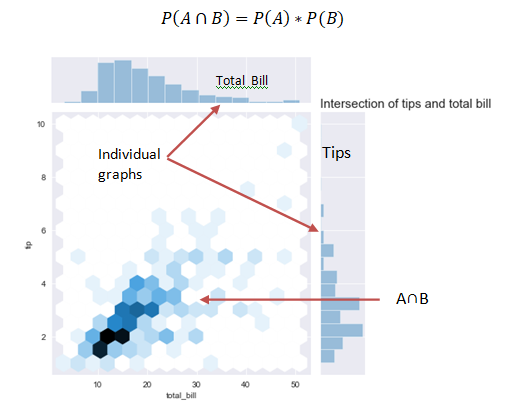
The law of multiplication is used to find the joint probability or the intersection i.e. the probability of two events occurring together at the same point of time.
In the above graph we see that when the bill is paid at the same time tip is also paid and the interaction of the two can be seen in the graph.
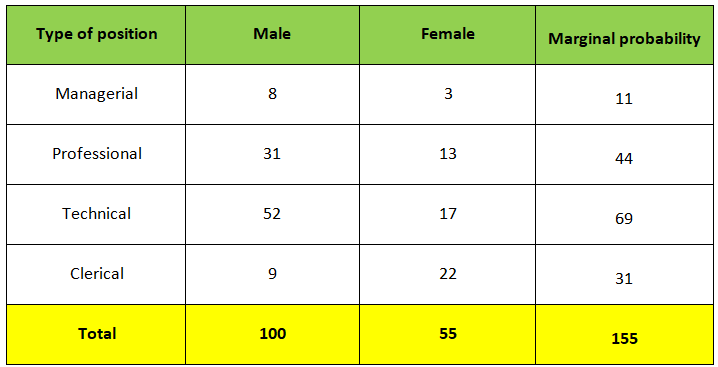
Joint probability table
A joint probability table displays the intersection (joint) probabilities along with the marginal probabilities of a given problem where the marginal probability is computed by dividing some subtotal by the whole.
Example:- Given the following joint probability table find out the probability that the employee is female or a professional worker.
Watch this video down below that further explains the theorems.
At the end of this blog, you must have grasped the basics of the theorems discussed here. Keep on tracking the Dexlab Analytics blog where you will find more discussions on topics related to Data Science training.
.
data science, Data Science Certification, Data Science Classes, Data Science Courses, data science online learning, Data Science training, Data Science training institute, Machine Learning, Machine Learning Certification, Machine Learning course, Machine Learning course in Gurgaon, Machine Learning course online, Machine Learning Courses, Machine Learning Training

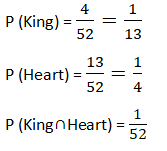
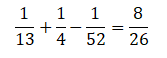

Comments are closed here.